- https://github.com/OWASP/MSTG-Hacking-Playground/wiki/Android-App#omtg_coding_004_code_injection
- https://github.com/OWASP/MSTG-Hacking-Playground/tree/master/Android/MSTG-Android-Java-App/app
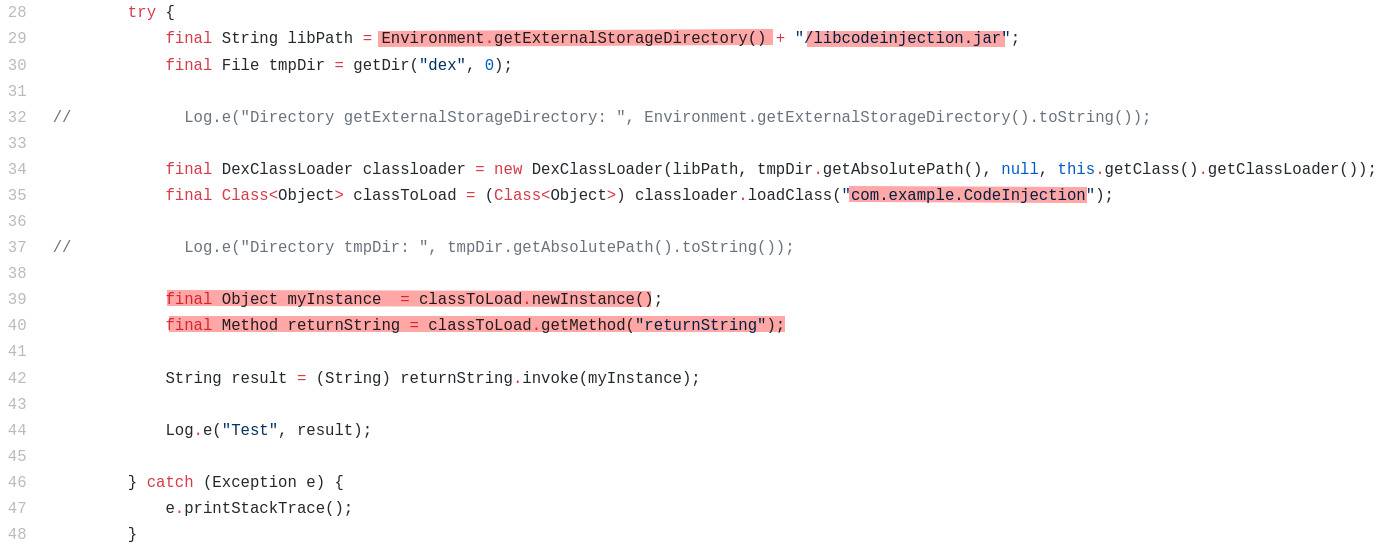
This activity is simulating Code Injection by using the Class DexClassLoader. A jar file called libcodeinjection.jar is dynamically loaded from the external storage and the class and it's function returnString() is executed.
The intent here is to show that loading of external JAR files dynamically is possible in Android. This should only be used very carefully and is not considered a best practice.
First of all we need to create the JAR. I’ll show you how to do it in Android Studio.
Start a new android studio project

In the editor File -> New -> New Module
Example code
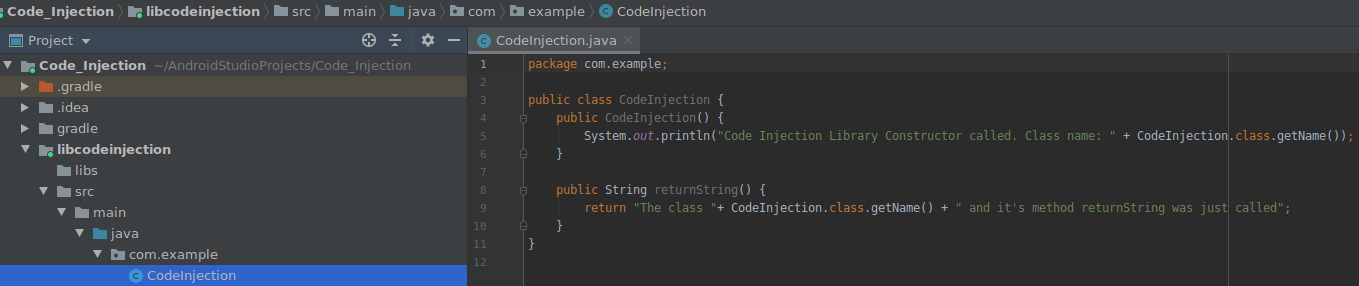
Building the JAR View -> Tool windows -> Gradle
Tasks -> build -> build (<- double click on it)
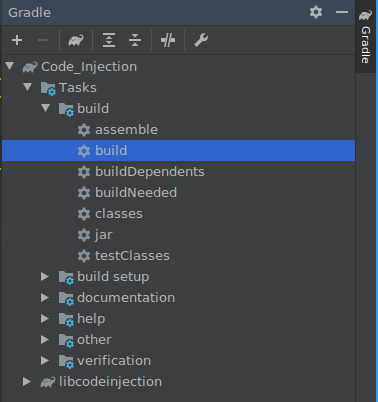
After building the JAR file should be here: AndroidStudioProjects/Code_Injection/libcodeinjection/build/libs/libcodeinjection.jar Copy it into your working directory.
The JAR needs to be in DEX format for the Android Platform, use dx from Android SDK for the conversion.
dx --dex --output=libcodeinjection.dex libcodeinjection.jar
Rename libcodeinjection.dex to classes.dex and pack it into a JAR again
mv libcodeinjection.dex classes.dex
jar cfv libcodeinjection.jar classes.dex
Push libcodeinjection.jar into the external storage of the target device with adb, the location in this case is /storage/emulated/0
adb push libcodeinjection.jar /storage/emulated/0
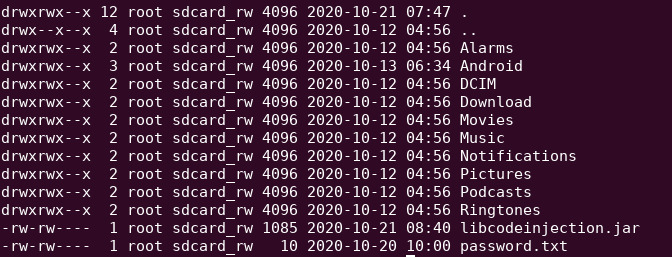
Check if the JAR is copied onto the target device
adb shell “ls -la /storage/emulated/0″
Open the application on the device and monitor the log
adb logcat | grep [pid]
Run activity OMTG_CODING_004_Code_Injection.
"The external JAR was successfully loaded from the external storage."
Logcat output

Tools used